Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
An advanced persistent threat apt can refer to a prolonged cyberattack where intruders gain access to the network and remain undetected for an extended period. The purpose of a capable attack is to steal sensitive data rather than to damage the targeted network. So, behind every apt attack, some highly skilled hackers have a specific target network and use a “low-and-slow approach” to intrude.

Table of contents
As per many survey reports, in 2022, 34% of companies worldwide experienced substantial technological mutilation and cyber security threat due to apt attacks. 68% of companies experienced a targeted attack on their network and loss of sensitive data. As per the market research, in 2021, the rate of attacks by apt on EU government agencies, large corporate houses, and institutions has increased by 30 percent.
In North America, advanced persistent threat (apt) protection is becoming a dominant market with a CAGR of 20.3%. It is assumed that the market share rate of apt protection in the US might increase to $6.64 million by 2025.
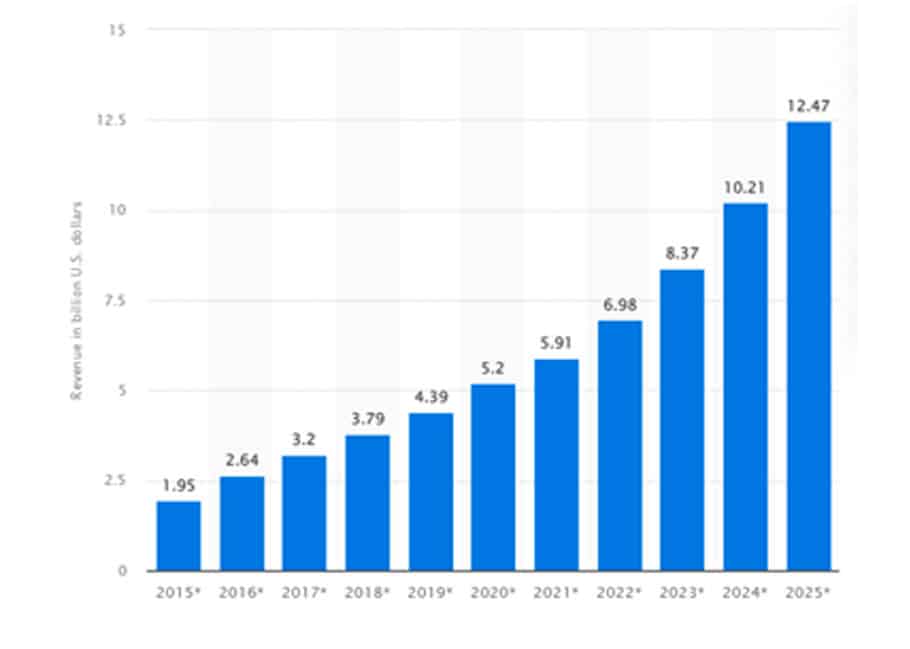
And at a global perspective, it is expected that by 2025, the advanced persistent threat protection market will be worth about 12.5 billion US$.
What is the advanced persistent threat?
The apt advanced persistent threat is a sneaky threat actor who gains access to a computer and targets the network in an unauthorized way. The definition of the term “apt” was traditionally associated with nation-state sponsorship. Though, in the last few years, multiple definitions and examples are coming from non-nation state groups.
In apt attacks, the primary aim of the threat actor is to get initial access to a computer and steal an organization’s sensitive data. As apt attacks used to be undetected for an extended period, the attackers can get enough time to go through the attack cycle and acquire primary objectives.
As the name carries the word “advanced”, it suggests the entire attacking/hacking process is clandestine and classy. The attacker remains inside your official network for a prolonged period, and you do not have any hunch about this presence. But, when you finally realize that your network is being hacked, it’s too late to protect your company from destructive consequences.
Execution of apt attacks needs a high degree of sophistication and customization. The apt actors used to spend extended periods and optimize resources at the targeted network to identify the organization’s vulnerability.
As per some cyber security experts, advanced persistent threat actors develop from “fine dining to junk foods”. Millions of threat actors have now adopted the tools and techniques once recognized by limited threat actors. For example, freelance groups are funded by government organizations. These groups arrange skilled cyber criminals who can use the complex hacking method to gain initial access to networks, collect sensitive data and threat intelligence, and steal intellectual property.
What is the phase of an APT attack?
To increase apt cyber security and develop advanced persistent threat solutions, you must recognize the Phases of an APT attack. The majority of the APT attack follows the same kind of life cycle. That is: invading a targeted network, getting initial access, stealing data, a spear-phishing email, and achieving the attack’s goal.
Now, let’s look at the three main phases of apt attack.
Phase 1: Infiltration
This is the first phase of the apt attack. At this phase, advanced persistent threats gain access to the targeted network via social engineering technology; one indication of an apt attack is a spear-phishing email that selectively targets high-profile networks. Attacking the emails of any specific individual is known as “spear-phishing emails“.
Phase 2: Escalation and Lateral Movement
Once the initial access has been obtained, the threat groups insert malicious Trojan or malware into the organizational network. Then move to the second phase, expansion. The apt groups are used to move laterally to map the network and allocate credentials like sensitive data, financial information, business information, etc.
Phase 3: Exfiltration
In the third phase of the apt attack, cybercriminals store the stolen information at a secret location within the targeted network. When enough data and information have been gathered, they “exfiltrate” it without being noticed. They use DoS or denial-of-service to distract the security team and clog the network while data is exfiltrated. The network remains vulnerable to such threats for an extended period.
What are the main characteristics of advanced persistent threats?
The main objectives of apt attacks can be distributed into four categories. These are:
- Hacktivism
- Cyber Espionage, which includes stealing Intellectual property and nation-state secrete
- Destructive
- eCrime for gaining financial benefits
The primary characteristic of an APT attack is that it uses sophisticated skills and methods to gain access to a network. Malware is an apt vector developed for use in apt attacks. For example, malware is used in agile sprints and for iteration in large software development projects.
Secondly, APT is a multi-phase attack that remains in your network for extended periods. The phase APT attacks include research, entry, mapping, and data collection.
Size is another crucial characteristic of apt attacks. Skilled cyber criminals or large organizations carry out these sophisticated and costly attacks. They either use this APT attack for the financial benefit or benefit of the nation, state, or political groups. Through apt, hackers usually capture a large amount of sensitive data.
Targeting is another important characteristic of apt attacks. This attack is highly targeted, and hackers are used to exploit organizational vulnerabilities. Hackers use extensive research to discover the weakness of your network setup and plan attacks accordingly.
Time frame is another essential characteristic of apt attacks. For conventional cyber attacks, like ransomware, the time required for the attack is used to be a week. But, advanced persistent threat attacks take extended time – a month or even a year.
Popular advanced persistent threats example
Some real-time advanced persistent threat examples are:
Large organizations and nations usually sponsor APT. An example of an apt attack includes the 2010 US and Israel cyber force attack on the Iranian nuclear program. The apt group aimed to restrict the country from dominating uranium storage. Stuxnet acted as the apt threat actor in this hacking process. The primary aim of this apt attack was to physically destroy the centrifugation of Iran that could enrich the country with uranium. Stuxnet was target specific Siemens industrial control system.
Hydraq can consider as another apt threat actor. It was used as an apt threat actor for Operation Aurora Campaign (2009). This high-profile network attack program targeted Google and other US-based companies. It was a china-based operation where a zero-day exploit was used to install the Hydraq, a malicious Trojan Horse.
In 2010, after one year, Google disclosed this attack. The threat victim of this apt attack were Adobe Systems, Rackspace, and Juniper Networks. Though apart from Google, no other US-based companies did not reveal this cyber attack publicly. Though, this attack’s threat vectors were diverse- from banks to the defence sector, security vendors to US-based oil and gas companies, and the technology sector of the United States.
How to detect an apt attack
Since Advanced Persistent Threats use different strategies and techniques to hack targeted networks, it always leaves some signs behind. Be it a normal apt attack or spear phishing email, the sign and symptoms of an advanced persistent threat attack include:
- Unusual activities in a personal account, such as increased level of login
- Higher level of presence of backdoor malware and Trojan
- Unexpected and heavy information flow. For example, anomalies in outbound information, a sudden increase in database operation involving massive amounts of data and information.
- Unexpected data bundles- can be a sign of data exfiltration.
As apt attacks are and used to be highly customized and sophisticated, they are challenging to detect. So, the question is how you or your company know you are the victim of apt. Let’s see the common warning sign of apt attacks in detail.
#1. Targeted Spear-phishing email
Hackers often use phishing attacks as a way to invade targeted emails. They used to select subjects likely to temper the employees and their interests. The topic or such mail can include an infected attachment or download link of any program that offers access to the hackers to your mail. This is known as a spear-phishing scam.
#2 Odd logins
Continuously track and assess your logins to your network. If you observe the rate of logins has increased suddenly even after working hours, or if you follow unusual patterns, that can be a serious concern.
#3. Moving of information
Hackers are in your system for some specific reason. You can detect whether your network is being hacked or not by seeing that a large batch of data is moving around. Files that you save in one drive but suddenly shift or move from one server to another. Keep an eye on unusual connections- if your answer is yes, you should know that your network is being hacked.
Advanced persistent threat solution
Today, 90 percent of the apt groups are using spear-phishing as an effective way to penetrate the internal organizational network. 48 percent of the apt groups are using legitimate administration tools and intellectual property regulation as a tool for advanced persistent threat solutions.
While detecting the apt attacks, increasing the apt security will be the best solution. Increasing the apt security can prevent the attack. For that reason, you have to perform penetration testing.
Penetration testing can help unleash your network’s vulnerability and test the ability to implement tools. In this process, you mimic attackers’ actions and methods to enter your network. In this testing process, one of the benefits is you can get immediate feedback on how you can improve the apt security.
Though, in the testing process, a few common flaws may restrict you from detecting and responding. For example, you often neglect endpoint security and put too much stress on malware. To increase the apt cyber security, you can follow the below steps:
- Shifting to an “already compromised” network
- Broadening the endpoint focus and visibility
- Increase the visibility of the entire attack in the network
To develop apt protection, you can increase focus on malicious activity rather than focusing on only prevention of infiltration. Falcon Insight endpoint detection and response is a tool with which you can detect IOAs and stop the attack before you lose valuable information. Falcon X is a solution aid that seamlessly integrates automated threat intelligence and customized indicator in endpoint protection.
Another effective way for Apt solution or to increase apts security is o limit the system access. You can use DiD or defense-in-depth to secure your network setup, and it uses internal firewalls and a traffic filtering setup. The principle of DiD is to provide specific and limited access to users and applications. As a result, it can limit the ability of hackers to traverse the target network.
To increase the apt security, you should keep your system up-to-date, which can help you significantly eliminate the incidence rate of apt attacks on your system. By updating your system, you can eliminate the vulnerabilities as the entry point of apt groups.
The APT attack starts with fraudulence with an email that acts as an entry point for hackers. With the implementation of the training program at your organization, you can instruct your employees about what to look for, what to do, and whom to contact if they notice any suspicious activity in email. The best way to reduce risks is to thwart attacks before they occur.
Conclusion
APT is a long-term, sophisticated cyber-attack. It relates to techniques and apt vectors, like zero-day attack, trojan, malware, lateral movement, etc. The goal of the APT attack is sabotage or manipulation of data, abuse of resources, reconnaissance for future attacks, stealing of administrative credentials, and so on.
This article gives you in-depth information about the APT attack and cyber security. This type of attack is mainly funded and designed by nation-state sponsorship. Considering the advanced persistent threat list, you can get an idea of how and why a nation or a state used to plan for an apt attack. Sometimes it is because of financial benefits, or sometimes it is a benefit for a nation or a state.
In apt attacks, the hackers mainly target the network of a large organization or governmental agencies. Though, in the past, it has become the most common event. Therefore, your responsibility should be aware of the apt attacks.
Keep your network updated, limit your network access and be aware of any malicious activities in your system. Working with a cyber security company can help you secure your network from hackers.